- Antradienis, Kovo 25, 2025
Wireshark is the world's leading network protocol analyzer, widely used for network troubleshooting, cybersecurity analysis, and protocol development. With support for over 2,500 protocols, it remains the industry standard for network traffic analysis and a trusted choice among professionals and researchers.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through installing Wireshark on Ubuntu 24.04, ensuring a clear, step-by-step approach that both beginners and experienced users can follow.
What is Wireshark?
Wireshark is an open-source network protocol analyzer that allows users to capture and analyze network traffic in real-time. It provides a detailed view of how data flows between devices, making it an essential tool for diagnosing network issues, monitoring performance, and identifying suspicious activity.
What is Wireshark Used For?
Wireshark is considered an essential tool for network professionals due to its ability to perform the following functions:
● Network troubleshooting – Identifying connection issues and diagnosing slow network performance.
● Cybersecurity analysis – Detecting suspicious traffic and potential security threats.
● Packet analysis – Understanding how different network protocols communicate.
● Performance monitoring – Analyzing bandwidth usage and identifying bottlenecks.
● Network forensics – Investigating past network activity and identifying potential attacks.
Now that we understand Wireshark’s role, let’s move on to installing it on Ubuntu 24.04.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding with the installation, ensure your system meets the following requirements:
● Ubuntu 24.04 Installed – This guide is specifically for Ubuntu 24.04. Bacloud engineers created and tested this tutorial with a KVM VPS server.
● Sudo Privileges – Administrative (root) access is required to install packages.
● Updated System – Keeping your system up-to-date prevents compatibility issues.
● Desktop Environment – Wireshark requires a desktop environment to run. If you're using a headless VPS, the GUI won't work. In that case, you’ll need to install a desktop environment or use TShark, the command-line alternative (see the note later in this guide).
Step 1: Update System Packages
Before installing any software, it's a best practice to update your system’s package list. This ensures you're getting the latest versions of dependencies and prevents conflicts.
Run the following command in your terminal:
|
sudo apt update && sudo apt full-upgrade -y |
This updates the package list and upgrades any outdated packages on your system.
Step 2: Install Wireshark on Ubuntu 24.04
Wireshark can be installed using two primary methods:
1. Using the Advanced Package Tool (APT) – This installs Wireshark from Ubuntu’s default repositories, ensuring stability and compatibility.
2. Using a Personal Package Archive (PPA) – This installs the latest stable version maintained by Wireshark developers.
Option 1: Install Wireshark via APT
The APT method is the easiest and most stable way to install Wireshark, as it uses Ubuntu’s default repositories. To install, run the following command:
|
sudo apt install wireshark -y |
During installation, you'll see a configuration prompt similar to the one below asking whether non-root users should be allowed to capture network traffic.
This is because Wireshark itself doesn’t capture packets, instead, it uses a separate tool called Dumpcap, which needs special permissions to access network interfaces.
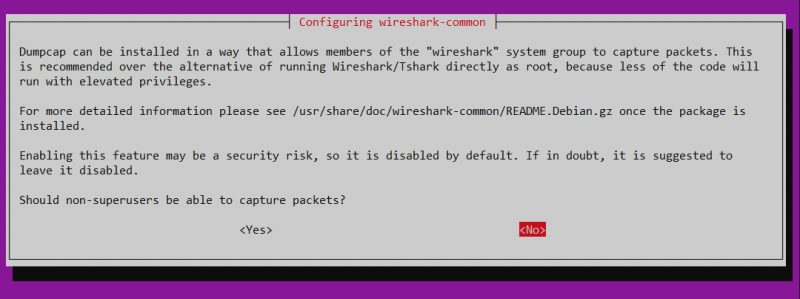
● If you select 'Yes,' non-root users will be able to capture packets, but you must manually grant them permission using the following command:
|
sudo usermod -aG wireshark $USER |
After running the command, restart your system or log out and back in for the changes to take effect.
● If you select 'No,' only the root user will have permission to capture packets. This means you must run Wireshark with sudo every time you use it:
|
sudo wireshark |
Option 2: Install Wireshark via PPA
If you need a more up-to-date version with the latest features and improvements, you can install Wireshark from the official PPA maintained by its developers.
To install via PPA, follow these steps:
1. Add the PPA repository:
|
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:wireshark-dev/stable -y |
This command adds the latest Wireshark package source to your system.
2. Update package lists:
|
sudo apt update |
This ensures Ubuntu recognizes the newly added PPA source.
3. Install Wireshark:
|
sudo apt install wireshark -y |
As with the APT method, you’ll be asked whether to allow non-root users to capture packets. Choose "Yes" if you want to use Wireshark without root access.
Now that Wireshark is installed, let’s verify it and launch the application.
Step 3: Verify the Installation
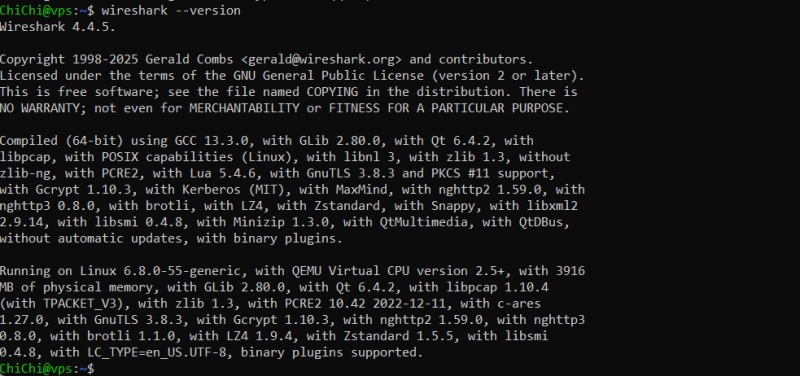
Before launching Wireshark, it's important to verify that the installation was successful. Run the following command to check the installed version:
|
wireshark --version |
If Wireshark is installed correctly, you should see an output similar to the one below displaying the installed version number. This confirms that Wireshark is ready to use.
Now that we've confirmed the installation, let's proceed to launching Wireshark.
Step 4: Launching Wireshark
Once Wireshark is installed, you can launch it either from the terminal or through the desktop interface, depending on your setup and preference.
Option 1: Using the Terminal
The simplest way to launch Wireshark is by running the following command in the terminal:
|
wireshark |
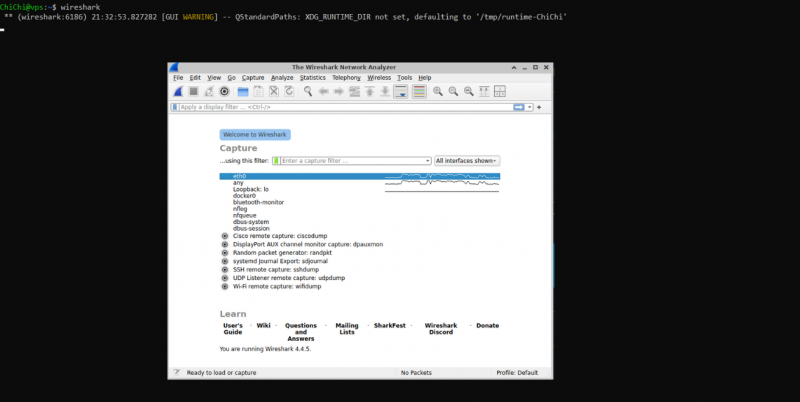
This will open the Wireshark GUI, allowing you to start capturing and analyzing network traffic.
Option 2: From the Desktop UI
If you prefer a graphical approach, you can launch Wireshark from the desktop interface. Open the Activities menu (or Applications menu, depending on your Ubuntu setup), search for 'Wireshark,' and click the Wireshark icon to launch the application.
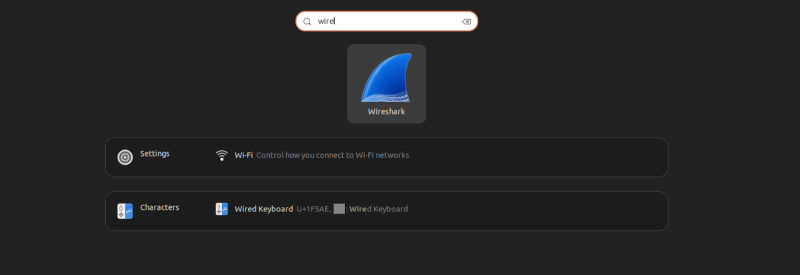
This method is ideal for users who are more comfortable using the graphical interface rather than using the command line.
Note: If you're running Ubuntu 24.04 on a headless VPS, the GUI version of Wireshark won’t work. Instead, use TShark, the command-line version of Wireshark:
|
tshark |
This allows you to capture and analyze packets directly in the terminal.
Step 5: Capturing Network Packets in Wireshark
After launching Wireshark, the next step is to capture network traffic. Wireshark provides a user-friendly interface to monitor and analyze data packets in real time.
1. Select a Network Interface
Before you start capturing packets, you need to select a network interface for monitoring, such as Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or a virtual adapter. On the main screen, you'll see a list of available interfaces, similar to the one below:
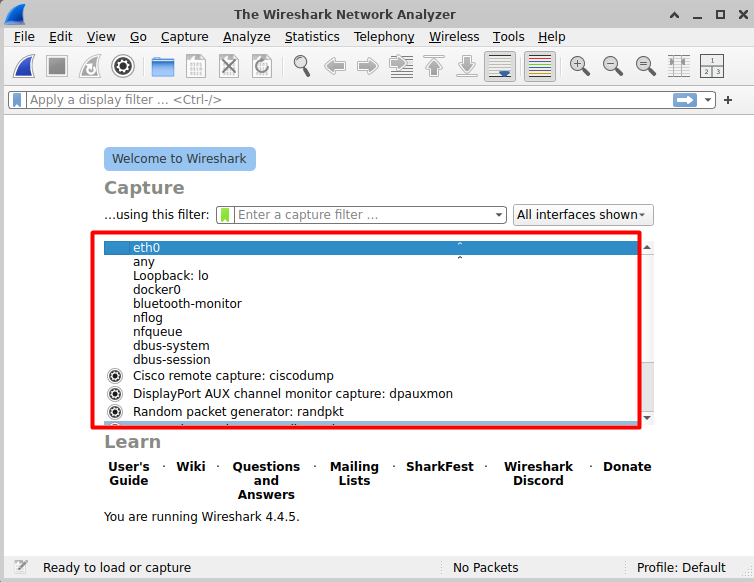
Click on the network interface you want to analyze. In the image above, eth0 is selected.
2. Start Capturing Packets
Click the Start button (a blue shark fin icon) to begin capturing live network traffic.
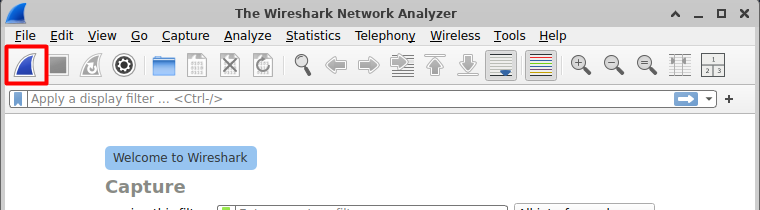
As soon as you start, Wireshark will display packets being transmitted and received on the selected interface.
3. Monitor the Packet Capture
The captured packets will appear in real time in a structured list like the one below:
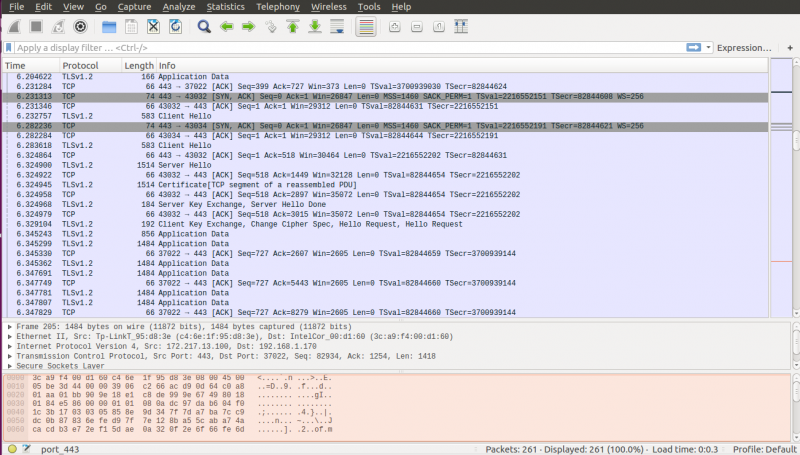
You can inspect packet details by clicking on any entry.
4. Stop Capturing Packets
When you’ve gathered enough data, click the Stop button (a red square icon) or press Ctrl + E.
5. Save Captured Packets
If you need to analyze the data later, go to File > Save As… Choose a location and save the capture as a .pcap file.
How to Uninstall Wireshark
If you need to remove Wireshark from your system, follow the steps below based on your installation method:
1. Uninstalling Wireshark Installed via APT
If you installed Wireshark using APT, remove it along with its configuration files by running:
|
sudo apt remove --purge wireshark -y |
2. Uninstalling Wireshark Installed via PPA
If you installed Wireshark using the Wireshark Developer PPA, start by removing the repository:
|
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:wireshark-dev/stable -y |
Next, uninstall Wireshark using the following command:
|
sudo apt remove --purge wireshark -y |
Cleaning Up Unused Dependencies
After uninstalling Wireshark, it's good practice to clean up any leftover dependencies and update your package list:
|
sudo apt update sudo apt autoremove -y |
Conclusion
Wireshark is a powerful tool for analyzing network traffic, and installing it on Ubuntu 24.04 is straightforward using either APT or a dedicated PPA. By following these steps, you can capture, inspect, and troubleshoot network packets. If needed, removing Wireshark is just as simple. Now that it’s set up, you can start analyzing network activity with confidence.
